CRR Relays for Functional Test Systems
Functional test systems continue to grow in size, pin count and complexity. Each pin usually requires 3 to 5 test connections. Each test connection needs to be isolated from all the others. Introducing any leakage paths thwarts the signals under test potentially shunting them to the point where they lose their functionality. Because of the high pin counts, the number of test connections grows dramatically. Here the need to satisfy these test connections with an ultra-small surface mounted relay (CRR series) becomes ideal with the following specifications:
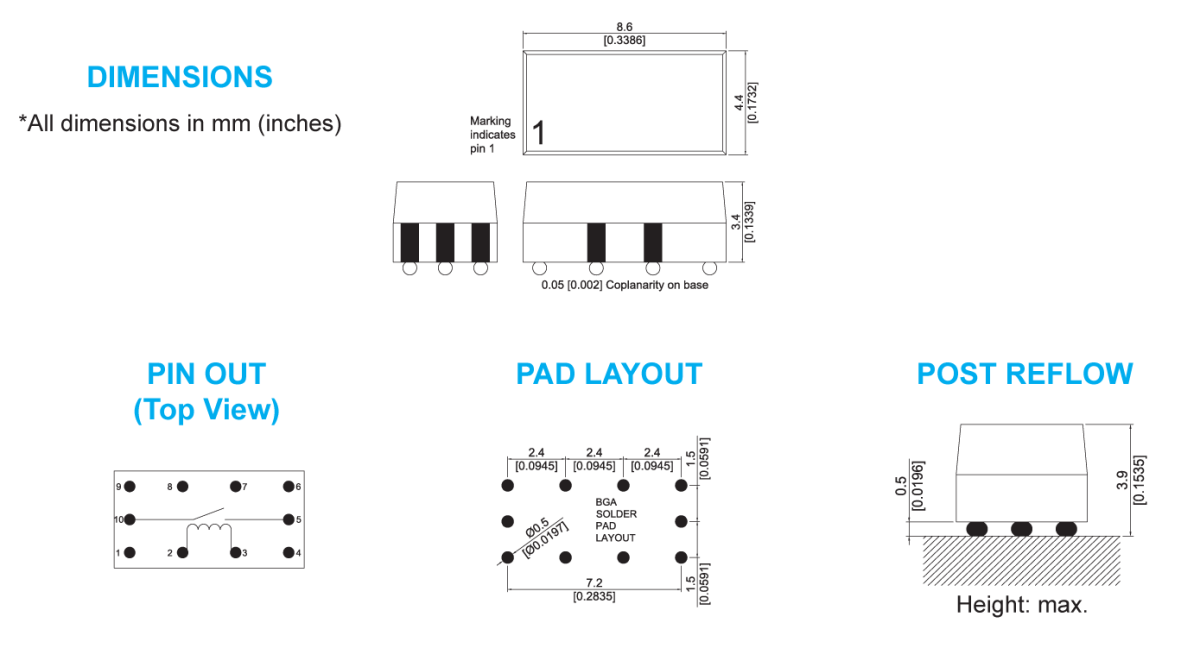
- Extremely small size (8.6 x 4.4 x 3.55 mm)
- Ability to mount the Reed Relays on both sides of the board
- Standard internal magnetic shielding eliminating any magnetic interaction even in the tightest matrices
- Insulation resistance to all points typically 1014 ohms
- Over 200 volts isolation across the contacts
- A minimum of 1500 volts isolation between switch and coil
- Thermal offset voltage across the contacts in the one microvolt or less range
- Contact capacitance is less than 0.2 pf
CRF Relays for Wafer, Memory, and Integrated Circuit Test Systems
Integrated circuit and wafer testers have continued to take on an ever more complex format with the need for faster and faster clock rates. With clock rates in the 2 GHz range, components must be able to pass continuous wave signals with frequency responses in the 8 to 10 GHz range. These fast-switching high speed digital signals require these new frequency responses
so that signals are not slewed or reflected going through the switching components in these systems.
The CRF Reed relay represents an ideal switch in these component testers for the following reasons:
- The frequency response of 7 GHz is a current critical need
- Rise time change through the relay of 40 picoseconds typical
- High return loss
- Insertion loss less than 1 dB at 6 GHz
- Extremely small size
- Ability to mount the Reed Relays on both sides of the board (with internal magnetic shielding eliminating any magnetic interaction)
- Insulation resistance to all points typically 1014 ohms
- Over 200 volts isolation across the contacts
- A minimum of 1500 volts between switch and coil
- Thermal offset voltage across the contacts in the one microvolt or less range
- Contact capacitance less than 0.2 pf
- Open contacts to shield capacitance 0.6 pf
Instrumentation (CRR and CRF)
- On measuring input of multimeters where voltage isolation is required, low voltage offsets (on the order of 1 microvolt or less) and very low sub-picoamp leakages are needed.
- Feedback loops where high frequency, low leakage, and voltage isolation are required
- In Attenuators where a high frequency response is required, low leakage paths are essential, long life (in excess of 100 million operations), and elimination of any inter-modular distortion is a clear need.
Multi-pole Configurations
When circuits require common points tied together, capacitance becomes a real problem. Trying to reduce this capacitance can be a real effort with no clear solution.
Using our new relay approach multipole relays with common tie points are no problem configuring with resulting reduced capacitance. Relay drivers, connectors, etc. can be easily added forming RF switching modules, RF attenuators, T/R switches, ‘T’ switches, etc.